Evaluate the quality of the services delivered

The quality control goal is to evaluate the quality of the services delivered, discover the defects and act for improvement – all by implementing the QA established processes. The following quality control activities will be systematically performed during the entire project lifecycle:
- Planning
- Reviews, Audits and Inspections
- Validation and Testing
- QA metrics calculation and analysis
- QA documentation management
The immediate “expression” of the project quality assurance is the Quality Assurance Plan, where we define, establish and enforce the proper quality assurance practices and activities. The QA Plan document defines:
- What is the targeted quality level
- What quality activities will be performed
- How do we measure the services/deliverables quality
- How do we (continuously) improve quality
- Specific roles and responsibilities
- Who, what, when and how
- Specific risks and mitigations

Reviews, Audits & Inspections
The key role of the quality assurance is to prevent incidents and defects. Therefore, it is critical to “advertise” the QA Plan as the main tool for incident prevention and to foster a proactive approach in maintaining the desired quality standards throughout the project lifecycle.
Reviews are very useful to identify and diagnose many systems problems. Security procedures, configurations, maintenance procedures etc. – they will all be reviewed in early phases, so we can act soon and minimize the high costs which are typically associated with issues that are discovered late in the game.
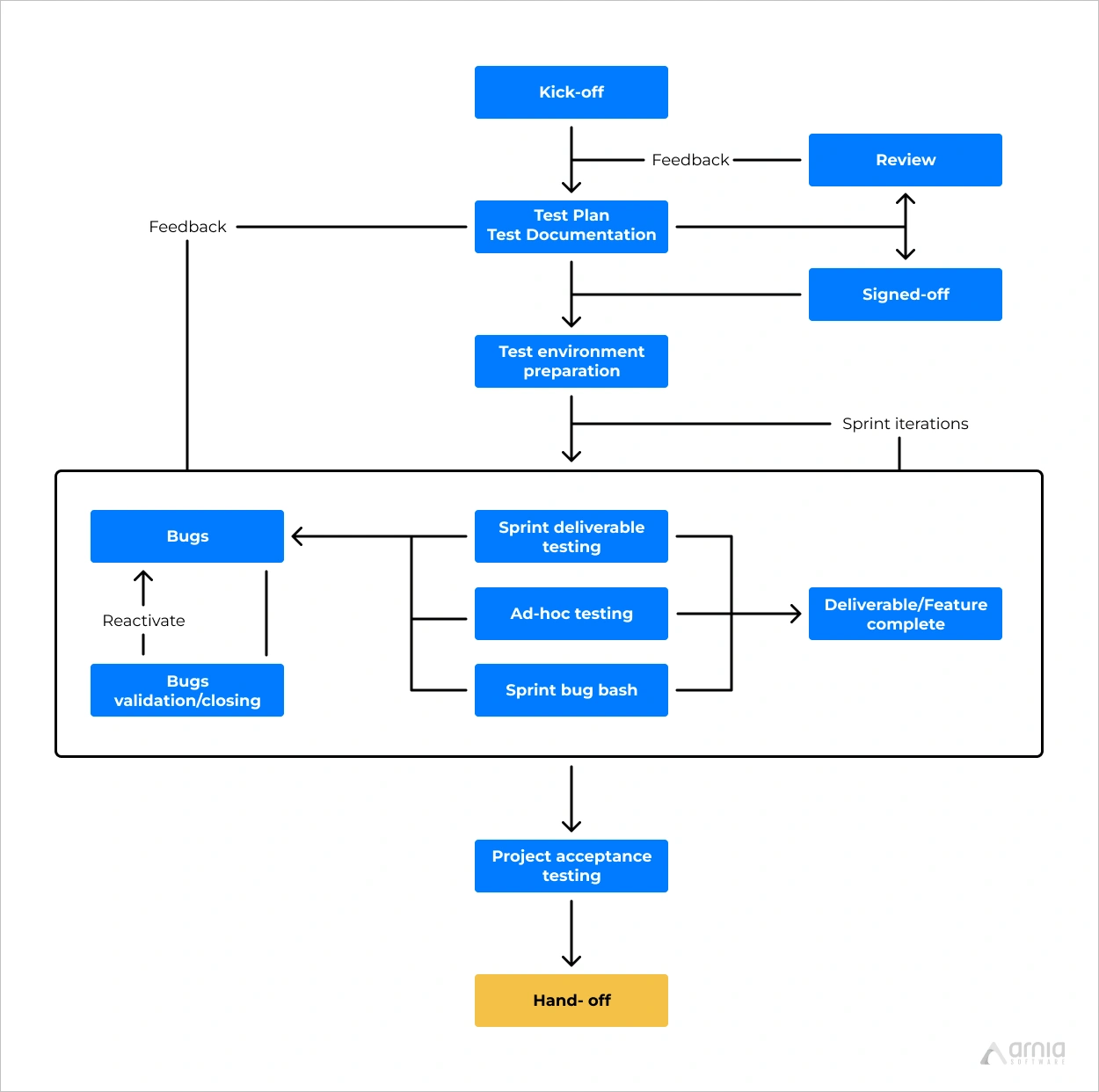
While reviews are usually performed in the design phase, audits and inspections are performed after the systems are up and running, but with the same ultimate goal – identify issues before they can cause disruptive effects and malfunctions. The following specific test activities will be executes periodically, during the entire project lifecycle:
- Planning
- Test planning and test design
- Test environment(s) setup
- Tests execution
- Analysis of the testing results
- Act for improvement
- Evaluation of the Sprints exit criteria
- Communication and feedback collection